General Biology II, lecture on Integration of Neural Systems
XVI. Central Neural Integration
A. Central Nervous system
1. Brain and spinal cord
2. integrating input from the peripheral nervous system
a. reflex arc
i. afferent (sensory) neurons bring signal to spinal cord
ii. interneurons (association) relay signal to
efferent (motor) neurons
(1) interneurons connect other neurons
iii. muscle contraction stimulated by efferent innervation
iv. many voluntary actions (e.g. walking) are reflexes
(1) brain is not necessary but may add information
3. Brain
a. specialized divisions with specialized function
i. increased development with evolutionarily increased
behavioral complexity
(1) hindbrain (e.g. medulla)- relatively unchanged
(a) regulates essential functions like breathing
(2) midbrain and diencephalon (e.g. hypothalamus)
- little changed
(a) regulates essential, but slightly variable
functions like reproduction, temperature, satiety
(b) produces neurotransmitters (DA, NE, 5-HT)
and neurohormones (GnRH, TRH)
(3) forebrain (e.g. cortex)- greatly increased in mass
in animals with increasingly complex behaviors
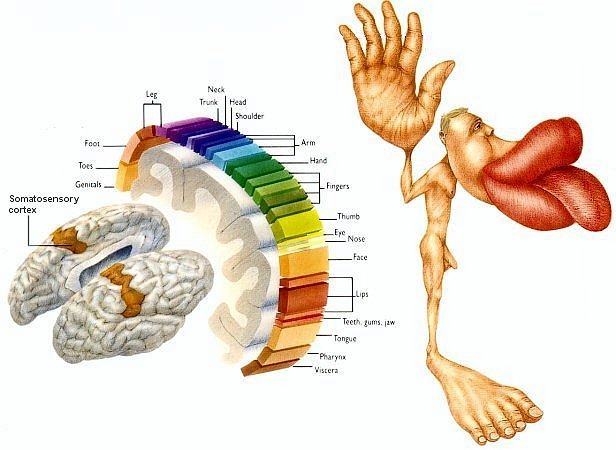
ii. cortex divided into gyri (ridges) each loosely
associated with specific functions
(1) e.g. Broca's area - speech
(2) areas related to sensory information from
each area of the body
(a) the more sensitive the area
the more brain allocated to it
B. Peripheral Nervous System
1. Autonomic Nervous System
a. sympathetic nervous system
i. secretes NE:
fight or flight: ®ñ heart rate, ñ blood pressure and ñ awareness,
¯ digestion, ¯ reproduction
b. parasympathetic ns
i. secretes ACh:
rest and digest: ¯ HR, ñ digestion
c. all internal organs and blood vessels are innervated by both
i. balanced
2. Somatic Nervous System
a. innervates skeletal muscle for voluntary movements
i. secretes ACh (acetylcholine)
ii. many voluntary movements do not require the brain